Clomiphene Testosterone Booster Calculator
Estimate potential testosterone increase when using clomiphene based on your current levels. Results are approximate and should be used under medical supervision.
Estimated Results
Results based on article information: clomiphene can raise testosterone levels by 30-80% in hypogonadal men without suppressing sperm production. Consult your physician before starting treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Clomiphene works by tricking the brain into releasing more LH and FSH, which stimulate natural testosterone production.
- It can raise testosterone levels by 30‑80% in hypogonadal men without shutting down sperm production.
- Typical dosing ranges from 25 mg to 50 mg taken every other day; adjustments depend on blood work and symptom response.
- Common side effects include visual disturbances, mood swings, and mild acne, while serious risks are rare.
- Regular monitoring of hormone levels, liver function, and semen analysis is essential for safe, effective use.
Imagine a medication that can lift your testosterone without the harsh suppression of traditional steroids. That’s exactly what Clomiphene for men promises: a gentle, oral pill that nudges the body’s own hormone system back into gear. While most people associate clomiphene with women’s fertility treatment, doctors have been prescribing it off‑label to men for years to address low testosterone and infertility.
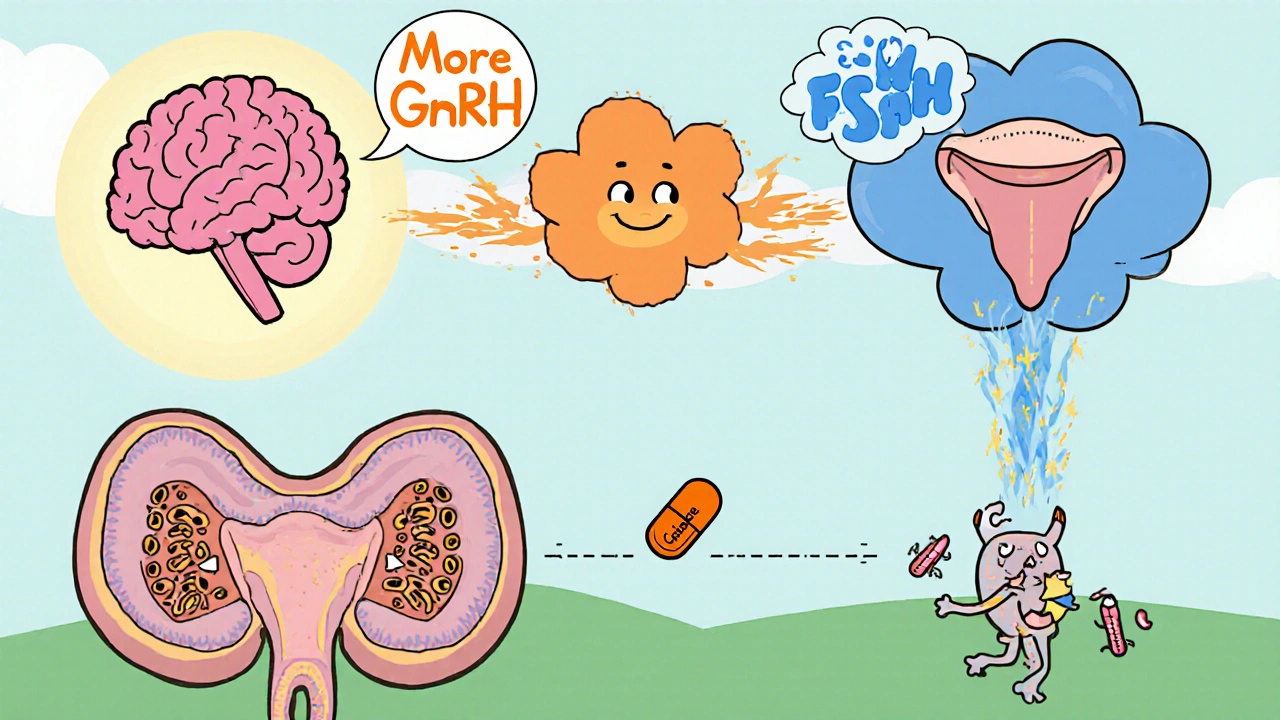
Clomiphene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) originally marketed under the brand name Clomid. It binds to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, blocking the negative feedback signal that estrogen normally provides. By doing so, the hypothalamus believes estrogen levels are low and releases more gonadotropin‑releasing hormone (GnRH), which in turn stimulates the pituitary to secrete two key hormones: luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle‑stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones travel to the testes, where LH tells Leydig cells to crank out testosterone and FSH supports spermatogenesis.
In men, the physiological cascade looks like this:
- Clomiphene blocks estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus.
- The hypothalamus releases more GnRH.
- The pituitary gland pumps out LH and FSH.
- LH stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone.
- FSH works with Sertoli cells to nurture sperm production.
Because the drug doesn’t supply external testosterone, the testes keep working, which is why sperm counts usually stay stable-or even improve-when clomiphene is used correctly.
Who Might Benefit?
Not every man with low testosterone is a good candidate. The sweet spot for clomiphene is the "functional hypogonadism" group: men whose testes are capable of producing testosterone but whose brain isn’t signaling them enough. Typical scenarios include:
- Men under 45 with mildly reduced testosterone (<300 ng/dL) and normal testicular size.
- Patients who want to preserve fertility while boosting libido, energy, or muscle mass.
- Those who have tried lifestyle changes (exercise, sleep, diet) with limited results.
- Individuals who experience side effects from traditional testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), such as testicular atrophy or suppressed sperm count.
Typical Dosing and How to Start
There’s no one‑size‑fits‑all schedule, but most clinicians begin with a low dose to gauge tolerance. A common starting point is 25 mg taken orally every other day. Blood tests are drawn after 4‑6 weeks to check total and free testosterone, LH, FSH, and estradiol.
If testosterone rises into the mid‑400 ng/dL range and the patient feels better, the dose may stay the same or be increased to 50 mg every other day. Some men respond well to a daily 25 mg regimen, especially if they have higher body mass or more severe suppression.
Key monitoring checkpoints:
- Baseline labs: total testosterone, free testosterone, LH, FSH, estradiol, CBC, liver enzymes.
- Repeat labs at 4‑6 weeks, then every 3‑6 months.
- Semen analysis before starting and after 3 months if fertility is a goal.

What to Expect: Results and Timeline
Most men notice a boost in energy, mood, and libido within 2‑4 weeks, but measurable testosterone changes often take 6‑8 weeks. Sperm parameters can improve as early as 8‑12 weeks, but a full 3‑month course is usually needed for meaningful fertility outcomes.
Studies from 2021‑2024 involving over 400 men show an average testosterone increase of 35‑80 ng/dL, with 70 % achieving levels above 500 ng/dL. Importantly, semen volume and motility either stayed steady or rose modestly, reinforcing clomiphene’s “fertility‑friendly” reputation.
Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Clomiphene is generally well‑tolerated, but no medication is risk‑free. Common, mild side effects include:
- Visual disturbances (blurred vision, spots) - usually reversible if the dose is lowered.
- Mood swings or irritability - can be mitigated with lifestyle stress‑reduction.
- Acne or oily skin - often improves after the first month.
Less frequent but more concerning issues are:
- Increased estradiol leading to gynecomastia - can be countered with a low‑dose aromatase inhibitor like anastrozole.
- Elevated liver enzymes - requires regular LFT monitoring.
- Thromboembolic events - extremely rare, mainly reported in men with pre‑existing clotting disorders.
If any visual symptoms appear, stop the drug and seek ophthalmologic evaluation immediately.
How Clomiphene Stacks with Other Therapies
Many men combine clomiphene with supplements or other prescriptions to fine‑tune results. Here’s a quick look at common combos:
| Booster | Mechanism | Typical Use | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clomiphene | SERM - raises LH/FSH | Low‑testosterone men wanting fertility | Oral, preserves sperm, no testicular atrophy | May raise estradiol, visual side effects |
| Exogenous Testosterone (gels, injections) | Direct hormone replacement | Severe hypogonadism, fast symptom relief | Predictable rise, strong symptom control | Spermatogenesis suppression, possible prostate issues |
| Selective Aromatase Inhibitors (anastrozole) | Blocks conversion of testosterone → estradiol | Men with high estrogen, adjunct to TRT | Boosts free testosterone, simple dosing | Can lower estrogen too much, bone health concerns |
| Herbal supplements (fenugreek, D‑aspartic acid) | Various, often weak LH stimulation | Gentle boost, low‑risk users | Natural, inexpensive | Inconsistent efficacy, limited research |
When stacking, keep a close eye on hormone panels. Adding an aromatase inhibitor can offset estrogen spikes from clomiphene, while zinc or vitamin D can support overall testicular health.
Safety Checklist Before Starting
- Confirm baseline testosterone < 400 ng/dL.
- Rule out primary testicular failure (e.g., very low LH/FSH).
- Screen for liver disease, clotting disorders, or uncontrolled hypertension.
- Discuss any history of visual problems or mood disorders with your physician.
- Ensure you are not using other SERMs or high‑dose estrogen blockers without supervision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can clomiphene replace testosterone replacement therapy?
Clomiphene can be an alternative for men who want to boost testosterone while preserving fertility. It works slower than direct testosterone gels, but it avoids testicular shrinkage and sperm suppression. Whether it replaces TRT depends on how low your levels are and how quickly you need symptom relief.
How long should I stay on clomiphene?
Most clinicians treat for 3‑6 months, then reassess. If testosterone stays in the target range and fertility goals are met, a gradual taper or drug holiday can be tried.
Will clomiphene affect my prostate?
Because clomiphene raises testosterone within normal physiological limits, prostate risk is similar to natural hormone levels. Still, men with a history of prostate cancer should avoid it and discuss alternatives with a urologist.
Do I need to take clomiphene every day?
Every‑other‑day dosing is common because the drug’s half‑life is long enough to maintain hormonal stimulation. Some doctors prescribe a daily low dose for men who metabolize the drug quickly.
Can I use clomiphene if I’m 50 or older?
It can work, but older men often have primary testicular failure, which means the pituitary can’t respond well. Hormone panels help decide; many doctors switch to TRT after age 45 if LH/FSH are low.
Bottom Line
Clomiphene offers a unique, oral route to boost testosterone while keeping the sperm factory running. With proper dosing, regular labs, and a clear eye on side effects, it’s a solid option for men who value both vitality and fertility. Always partner with a qualified physician who can tailor the protocol to your labs and goals.





Vikas Kumar
October 23, 2025 AT 15:17Our nation’s men deserve a home‑grown solution, not a cocktail of foreign steroids that leaves them dependent on the West. Clomiphene offers a domestic, oral option that respects our bodies while keeping our bloodlines strong. By nudging the brain to release more LH and FSH, it lets the testes do their job without external interference. This is the kind of self‑reliant therapy that aligns with our cultural pride. If you’re serious about restoring vigor, consider the Indian‑approved protocols and stay true to your roots.
Celeste Flynn
November 2, 2025 AT 13:10Clomiphene can really help men who have low testosterone levels especially when the testes are still healthy it works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus which tricks the brain into releasing more GnRH and then LH and FSH this cascade boosts natural testosterone production without shutting down sperm production it's a safe option if monitored regularly
Shan Reddy
November 12, 2025 AT 12:03From a mechanistic standpoint, clomiphene acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator, so it essentially “lies” to the hypothalamus about estrogen levels. This prompts the pituitary to increase LH and FSH output, which directly stimulates Leydig cells to make testosterone. The benefit here is that spermatogenesis remains intact because the testes are still receiving FSH signaling. Regular bloodwork will tell you if the dosage needs tweaking. Overall, it’s a fairly elegant physiological hack.
CASEY PERRY
November 22, 2025 AT 10:57Clomiphene functions as a SERM, antagonizing hypothalamic ERα and upregulating GnRH pulsatility. The resultant increase in LH/FSH drives Leydig cell steroidogenesis while preserving Sertoli‑cell mediated spermatogenesis. Clinical titration typically ranges 25‑50 mg every other day, guided by serum testosterone and semen parameters.
Naomi Shimberg
December 2, 2025 AT 09:50While the prevailing literature extols clomiphene as a panacea for functional hypogonadism, one must consider the paucity of long‑term safety data in diverse populations. The pharmacologic manipulation of the hypothalamic‑pituitary‑testicular axis could precipitate unforeseen endocrine feedback loops. Moreover, the cited testosterone increments, albeit statistically significant, may not translate into clinically meaningful outcomes for all cohorts. Consequently, a cautious, individualized approach remains advisable.
kenny lastimosa
December 12, 2025 AT 08:43It is tempting to view clomiphene merely as a chemical lever, a tool that flips a switch in the endocrine circuitry, yet such a reductionist perspective overlooks the subtle interplay of mind, body, and environment that underlies hormonal balance. When one considers the evolutionary context of the hypothalamic‑pituitary–testicular axis, it becomes apparent that any intervention is, in a sense, a dialogue with an ancient system rather than a unilateral command. The drug’s role as a selective estrogen receptor modulator introduces a nuanced form of feedback that mirrors natural fluctuations, allowing the testes to retain their intrinsic capacity for spermatogenesis. This is not merely a pharmacological curiosity; it speaks to a broader philosophical question about the extent to which we should augment versus cooperate with our physiology. In the realm of bioethics, the distinction between restoration and enhancement blurs, prompting us to reflect on what constitutes authentic vitality. Moreover, the variability in individual response reminds us that the human organism resists homogenization, defying the one‑size‑fits‑all model that some clinicians may unintentionally endorse. While serum testosterone may rise by thirty to eighty percent in certain cases, the subjective experience of vigor can be mediated by factors such as sleep quality, psychological stress, and nutritional status. Thus, a holistic appraisal that integrates lifestyle modifications alongside clomiphene therapy is likely to yield more sustainable outcomes. From a pragmatic standpoint, regular monitoring of liver function and semen parameters serves not only as a safety net but also as a feedback mechanism for dose adjustment, reinforcing the collaborative nature of treatment. The interplay of LH and FSH with Leydig and Sertoli cells exemplifies a symphony of signals, each contributing to the final composition of hormonal health. Recognizing this complexity encourages humility in our clinical prescriptions, reminding us that we are custodians rather than masters of the endocrine orchestra. In conclusion, while clomiphene offers a valuable option for men grappling with functional hypogonadism, its use should be contextualized within a broader framework that honors both the science and the philosophy of human well‑being.
Heather ehlschide
December 22, 2025 AT 07:37Building on that thoughtful overview, it’s worth noting that baseline semen analysis before initiating clomiphene can help distinguish true improvement from natural variability. Additionally, checking estradiol levels occasionally can prevent potential estrogenic side effects that occasionally emerge with higher doses. Adjustments are usually made in 12.5 mg increments, guided by both lab results and symptom tracking.
Dan Danuts
January 1, 2026 AT 06:30Hey folks, just wanted to say that I tried clomiphene a few months back after my doc recommended it for low T. I felt more energy and my mood was steadier, plus my sperm count stayed solid. If you’re on the fence, give the regular blood checks a shot and you’ll know if it’s working for you. Keep pushing forward, guys!
keerthi yeligay
January 11, 2026 AT 05:23Clomiphne is easy to use just 25 mg evry other day and you can see results in 6-8 weeks if you stay on track.
Peter Richmond
January 21, 2026 AT 04:17Regular monitoring of hepatic enzymes and semen parameters is essential to ensure therapeutic efficacy while mitigating adverse effects.
Tristram Torres
January 31, 2026 AT 03:10If you’re not willing to get blood work done, you’re basically gambling with your fertility.
Jinny Shin
February 10, 2026 AT 02:03The narrative around “quick fixes” often obscures the nuanced reality of hormonal health, leaving many disillusioned.
deepak tanwar
February 20, 2026 AT 00:57Despite the enthusiasm surrounding off‑label use, the lack of large‑scale randomized trials warrants a skeptical stance before widespread adoption.